Introduction
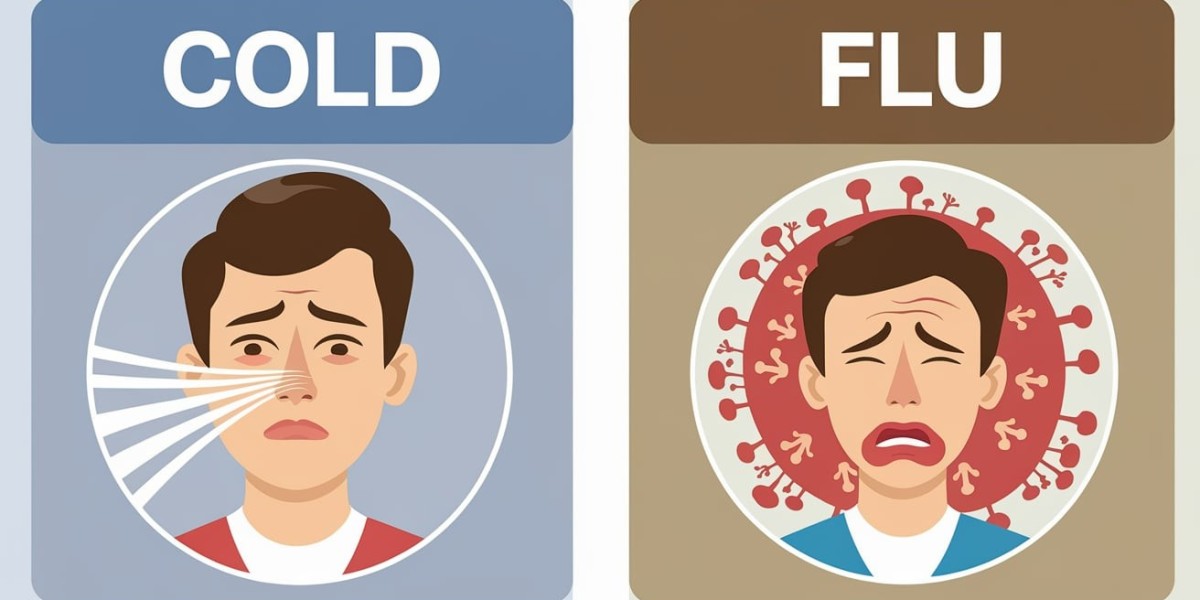
Seasonal illnesses like the flu and the common cold often create confusion due to their overlapping symptoms. Many people struggle to differentiate between the two, leading to mistreatment or unnecessary concern. Understanding their distinctions is crucial for managing symptoms effectively and seeking appropriate medical care. A precise diagnosis not only ensures the right treatment but also helps prevent complications that may arise from severe infections.
What Causes the Flu and the Common Cold?
Both flu and cold are viral infections, but they stem from different pathogens. The influenza virus causes the flu, while the common cold is triggered by several types of viruses, most commonly rhinoviruses.
These viruses spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person sneezes, coughs, or talks. They can also be contracted by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the face. While both illnesses share transmission methods, the flu tends to be more severe due to the aggressive nature of the influenza virus.
Key Differences Between Flu and Cold Symptoms
One of the key distinctions between flu and cold is how the symptoms develop. Flu symptoms appear suddenly and can be intense, while cold symptoms emerge gradually and are generally mild.
The severity also varies. Flu often brings high fever, body aches, and extreme fatigue, whereas a cold usually results in a runny nose, mild sore throat, and congestion. The duration of illness is another indicator. Colds typically last a few days to a week, while flu symptoms can persist for up to two weeks or longer in severe cases.
Flu Symptoms: What to Look Out For
High fever and chills are common flu symptoms, making sufferers feel weak and uncomfortable. Body aches and extreme fatigue can be debilitating, making even simple daily tasks challenging. The flu also affects the respiratory system, causing a severe cough and significant chest discomfort. These symptoms can escalate, leading to complications like pneumonia if not managed properly.
Cold Symptoms: How They Differ from the Flu
Unlike flu, a cold predominantly affects the nasal passages. A runny or stuffy nose is a telltale sign of a cold, often accompanied by mild throat irritation. Coughing in colds is typically mild and does not persist as long as flu-induced coughing. Sneezing and nasal congestion are also primary indicators, making colds more of an annoyance than a debilitating illness.
Overlapping Symptoms: When It’s Hard to Tell
Certain symptoms make it difficult to distinguish between flu and cold. Fever is a major factor—while common in flu, it is rare in colds. Coughing is another shared symptom, but flu-related coughs tend to be more severe and prolonged. Fatigue levels differ as well; colds may cause slight tiredness, whereas flu leads to extreme exhaustion that can last for weeks.
How to Tell if You Have the Flu or a Cold
A self-assessment can help determine whether you have flu or a cold. Monitoring symptom intensity and onset speed is crucial. If symptoms appear suddenly with fever and body aches, flu is more likely. Using a thermometer to check fever levels can also provide clarity—flu-related fevers are often high, while colds rarely cause a significant temperature increase.
Risk Factors: Who Is More Vulnerable to Severe Illness?
Certain groups are at higher risk for flu complications, including young children, the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions such as asthma or diabetes. These individuals should take extra precautions, as flu can lead to severe complications such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
Treatment Options for Flu and Cold
Over-the-counter medications can alleviate symptoms but do not cure the infection. Pain relievers, decongestants, and cough syrups can provide relief. Home remedies such as warm teas, honey, and steam inhalation may also help. For severe flu cases, prescription antiviral drugs like Tamiflu can reduce symptom severity and duration.
Preventing the Flu and Common Cold
Flu vaccination is one of the most effective prevention methods, significantly reducing the risk of infection. Practicing good hand hygiene by frequently washing hands with soap and water can prevent viral spread. Strengthening the immune system through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep further enhances the body's ability to fight infections.
When to See a Doctor for Flu or Cold Symptoms
Certain symptoms require medical attention. If flu symptoms persist beyond ten days, or if they worsen suddenly, seeking medical care is crucial. Complications like pneumonia, bronchitis, or sinus infections can arise if left untreated. Lingering high fever, severe chest pain, or breathing difficulties should never be ignored.
24-Hour Chemists on the Gold Coast – Where to Find Help Anytime
During flu and cold season, access to medication and medical advice is essential. 24-hour pharmacies on the Gold Coast provide round-the-clock support for those needing relief at odd hours. Several reputable chemists in the area offer flu medication, pain relievers, and consultation services. These facilities ensure that individuals can manage their symptoms effectively, regardless of the time of day.
Conclusion
Recognizing the differences between flu and cold helps individuals take the right course of action for faster recovery. Early recognition of symptoms, coupled with proper care, reduces the risk of complications. Preventive measures, including vaccination and good hygiene, are key to avoiding seasonal illnesses and maintaining overall well-being.