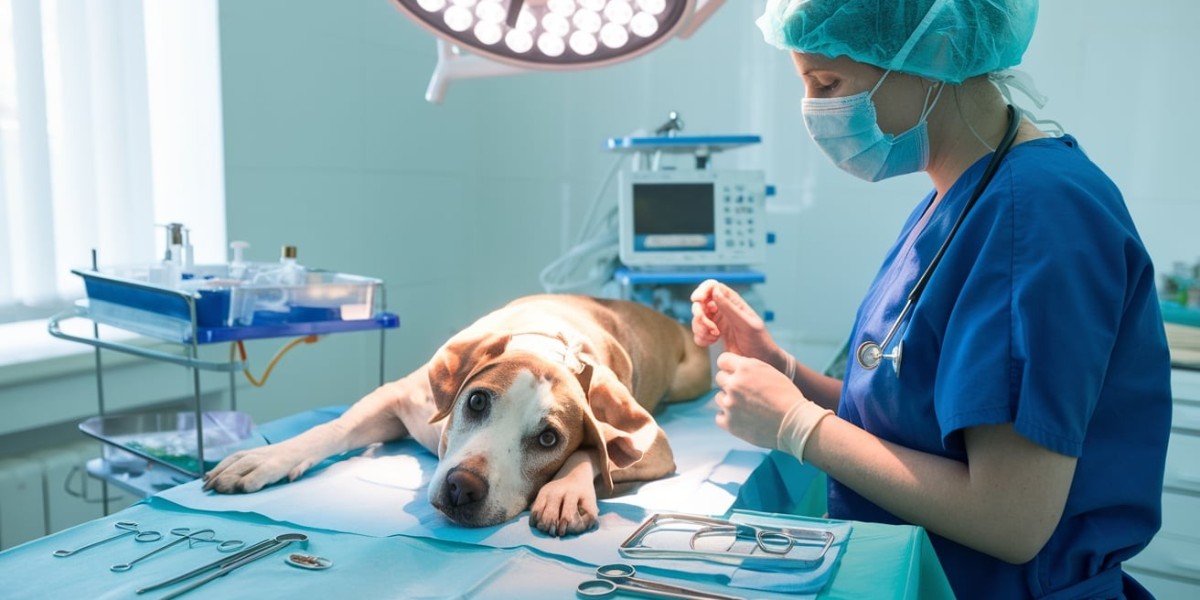
The Importance of Safe Anesthesia in Canine Surgeries
Ensuring the safety and comfort of canine patients during surgical procedures is paramount in veterinary medicine. A critical component of this process is the administration of anesthesia, which not only facilitates pain-free surgeries but also minimizes stress and potential complications.
Why Anesthesia is Crucial for Pain-Free Procedures
Anesthesia serves as the cornerstone of humane veterinary care, rendering surgical interventions pain-free and tolerable for canine patients. By inducing a reversible state of unconsciousness, anesthesia ensures that dogs do not experience pain or distress during procedures, thereby upholding ethical standards and promoting optimal recovery.
The Role of Anesthesia in Minimizing Surgical Stress
Beyond pain management, anesthesia plays a pivotal role in mitigating surgical stress. It suppresses involuntary movements and physiological responses to surgical stimuli, such as elevated heart rate and blood pressure, thereby creating a stable environment for both the patient and the surgical team.
Pre-Surgical Assessments: Preparing Your Dog for Anesthesia
Comprehensive Health Evaluations Before Surgery
Prior to administering anesthesia, a thorough health evaluation is imperative. This assessment includes reviewing the dog's medical history, conducting physical examinations, and performing diagnostic tests to identify any underlying conditions that could influence anesthetic risk.
Identifying Potential Risk Factors in Individual Dogs
Individual factors such as age, breed, weight, and pre-existing medical conditions can significantly affect a dog's response to anesthesia. For instance, brachycephalic breeds like Bulldogs may have anatomical challenges that increase anesthetic risk. Recognizing these factors allows veterinarians to tailor anesthesia protocols accordingly.
Customized Anesthetic Plans: Tailoring Protocols to Individual Dogs
Factors Influencing Anesthetic Choices
Anesthetic plans are customized based on various factors, including the dog's health status, the nature of the surgical procedure, and potential drug interactions. This individualized approach enhances the safety and efficacy of anesthesia.
Developing Personalized Anesthesia Strategies
By integrating the pre-surgical assessment findings, veterinarians develop personalized anesthesia strategies that encompass drug selection, dosing, and monitoring plans, ensuring a tailored approach to each canine patient.
Sedation and Premedication: Setting the Stage for Smooth Anesthesia
Common Sedatives and Their Effects
Sedation and premedication are employed to calm dogs before induction, reducing anxiety and facilitating smoother anesthesia induction. Common sedatives include agents like dexmedetomidine and midazolam, which provide calming effects and muscle relaxation.
Benefits of Premedication in Reducing Anxiety and Pain
Premedication not only alleviates anxiety but also contributes to multimodal pain management, reducing the required doses of anesthetic agents and enhancing overall patient comfort.
Induction of Anesthesia: Transitioning Dogs into Unconsciousness
Techniques for Safe and Effective Induction
Induction involves administering anesthetic agents to transition the dog from consciousness to an unconscious state suitable for vet surgery . Techniques may include intravenous injection or inhalation methods, chosen based on the patient's needs and the procedure's requirements.
Medications Commonly Used During Induction
Agents such as propofol and alfaxalone are commonly used for induction due to their rapid onset and short duration of action, allowing for precise control over the anesthetic state.
Maintaining Anesthesia: Keeping Dogs Stable During Surgery
Monitoring Vital Signs and Depth of Anesthesia
During surgery, continuous monitoring of vital signs—including heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation—is essential to assess the depth of anesthesia and the patient's physiological status.
Adjusting Anesthetic Levels for Optimal Safety
Based on monitoring data, anesthetic levels can be adjusted in real-time to maintain an appropriate depth of anesthesia, ensuring the dog's stability and minimizing the risk of complications.
Balanced Anesthesia: Combining Agents for Optimal Outcomes
Advantages of Using Multiple Anesthetic Agents
Balanced anesthesia involves using a combination of anesthetic agents to achieve the desired effects while minimizing adverse reactions. This approach allows for lower doses of individual drugs, reducing potential side effects and enhancing patient safety.
How Balanced Anesthesia Reduces Complications
By targeting different pathways involved in pain and consciousness, balanced anesthesia provides comprehensive management, leading to smoother inductions, stable maintenance, and expedited recoveries.
Monitoring During Surgery: Ensuring Safety in Real-Time
Essential Monitoring Equipment and Techniques
Utilizing advanced monitoring equipment, such as electrocardiograms (ECG), capnography, and pulse oximetry, enables real-time assessment of the dog's physiological parameters, facilitating prompt detection of any anomalies.
Recognizing and Addressing Intraoperative Complications
Vigilant monitoring allows the surgical team to swiftly identify and address intraoperative complications, such as hypotension or hypoventilation, thereby enhancing the safety and success of the procedure.
Post-Anesthetic Care: Supporting Recovery After Surgery
Strategies for Smooth and Comfortable Recoveries
Post-anesthetic care focuses on ensuring a smooth transition from anesthesia to full consciousness. This includes monitoring vital signs, providing warmth, and administering analgesics to manage pain effectively.
Managing Potential Post-Anesthetic Issues
Some dogs may experience temporary disorientation, nausea, or vocalization post-anesthesia. Veterinary teams are trained to manage these issues promptly, ensuring a comfortable recovery period for each patient.
Conclusion: Ensuring Safe Anesthesia for Every Canine Patient
Safe anesthesia in canine surgeries is a collaborative effort that requires meticulous planning, careful drug selection, continuous monitoring, and post-operative care. Veterinarians play a crucial role in ensuring that each patient receives an individualized anesthetic plan, tailored to their specific needs and health conditions. Pet owners, too, play an integral part by understanding the importance of pre-surgical assessments, following post-operative care guidelines, and communicating any concerns with their veterinary team.
Advancements in veterinary anesthesia continue to improve safety and efficacy, reducing risks and enhancing the overall surgical experience for dogs. By prioritizing safety, education, and innovation, veterinary professionals can ensure that anesthesia remains a reliable and effective tool in providing pain-free, stress-free surgical procedures for canine patients. Through this ongoing commitment, we can uphold the highest standards of veterinary care, ensuring that every dog receives the best possible outcome during surgical interventions.